What is 32-bit audio and why does it matter?
In 2019, Sound Devices introduced the world’s first 32-bit audio interface: The MixPre II series.
32-bit floating point recording format is not new. Pro Tools and Logic Pro X for example operate as a “32-bit floating point” recording format. What IS new is a USB audio interface that offers 32-bit audio for MacOS and Windows 10.
What does this mean?
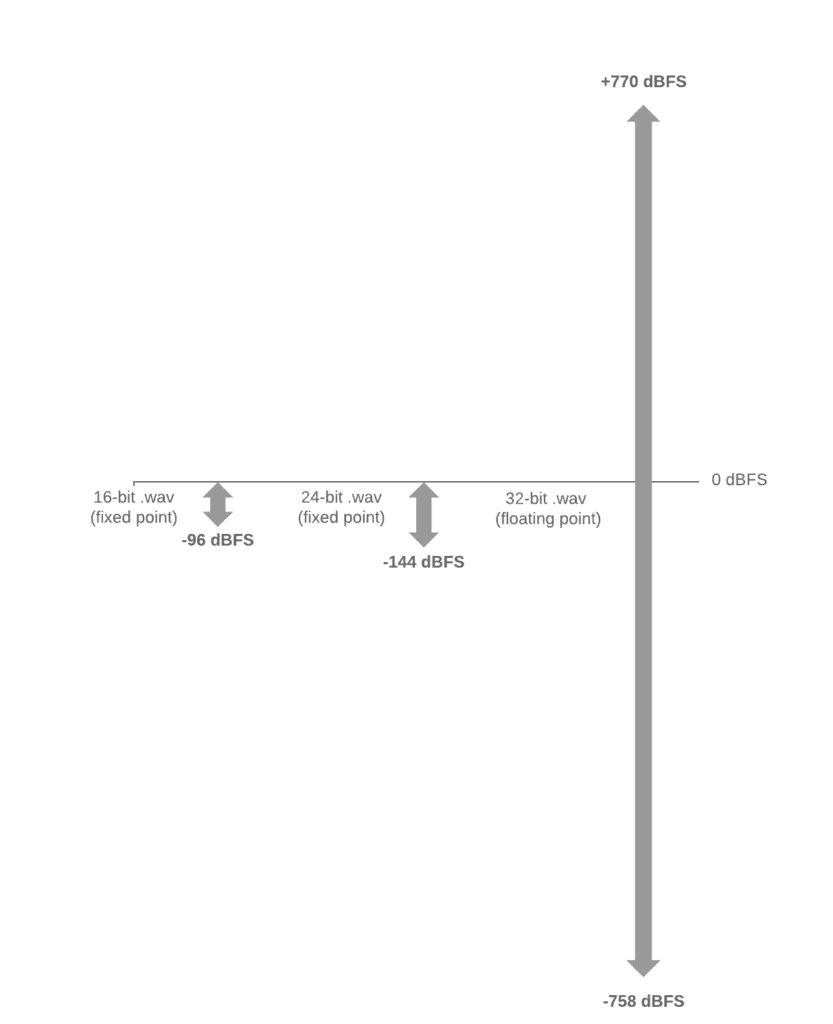
In simple terms, when recording in 24-bit audio (which is the current, most widely used format), you can only turn the audio up to “0 dBFS”. In other words, “0” is the ceiling. If you go past “0”, the audio is clipped and distorted.
With 32-bit audio, if the signal recorded is “clipped” or past”0 dBFS”, you can go into your DAW after the fact and turn it down and the signal will be as pristine as if you never “clipped”. Because with 32-bit audio, you have 770 dB of more headroom. Just writing that made me pause! I have been in the audio industry for over 20 years and I am still trying to wrap my head around this incredible statement!
From: https://www.sounddevices.com/32-bit-float-files-explained/:
Think about the possibilities this opens up for audio engineers everywhere!
Let’s say you are on location and responsible for the audio of a commercial being shot. The actors finally get that perfect take, the director is thrilled and then… they notice your audio was clipped and what would be considered “ruined” in the 16-bit or 24-bit world, with 32-bit, no problem. In fact, you don’t even have to set levels going into recording! The levels are set in post.
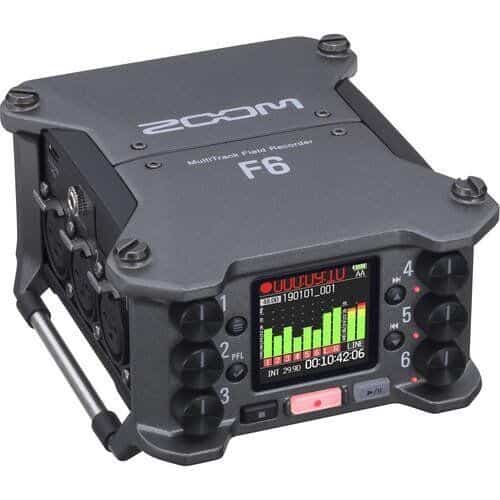
Since the release of Sound Devices “MixPreII” in 2019, other companies have followed. For field recording, Zoom released the ZOOM F6, the first professional field recording to feature both 32-bit audio and dual A/D converters:
It’s important to note that as long as the source is clean, your 32-bit signal will be clean and can be adjusted. However, it is still possible to have irreparable distortion even in 32-bit audio.
How?
Many years ago, the company I was interning with was recording a large choir at a local University hall. As we were getting levels, my mentor noticed that we were getting distortion from the soprano section. Young and eager to help, I replied: “Ok, I will pad it”, reached over to the mic preamp, and proceeded to switch on the “10dB” pad. My mentor quickly prevented me from engaging the pad switch on the mic preamp. He said: “That won’t fix it. Even if you did pad it from the mic preamp, you are still going to get distortion because it is distorting at the source!”
He went on to educate me: “Remember SPL: Sound Pressure Level. If the SPL is greater than the capsule can handle, then distortion happens at the capsule, not at the preamp. So, pad at the mic.”
I engaged the 10dB pad on the actual microphone. My mentor was right; no more distortion!
This lesson reminds me that if you still are distorting at the capsule, no amount of bits will be able to fix this in post. You would have to resort to audio repair software such as iZotope RX series. As good as that is, even that might not be able to repair it and even if it could repair it will never be as good as a purely sourced signal.
In summary, 32-bit audio provides a worry-free recording experience for the Audio Engineer. Now, Audio Engineers can focus their attention on other aspects of recording instead of spending time and energy riding a fader with one hand to prevent levels from clipping and nervously wiping the sweat from their brow with the other.
You can expect to see all other audio interfaces, from UA Apollo, Focusrite Scarlett, etc to release their own version of 32-bit audio in the coming years.
Summary
What: 32-bit floating point audio interface
Why it matters: You don’t have to worry about “clipping” audio. Just push record, capture the sound, and adjust levels in post-production.
What it means for the future of audio:
- We can expect all other audio companies to follow suit, introducing their own version of 32-bit audio interfaces.
- Audio Engineers can focus on other important aspects of recording and not worry about levels that may clip since they can be readjusted in post production while retaining fidelity.
Is it possible that you can still have distorted audio in a 32-bit floating point audio interface?
Sure is. If your signal is distorting at the capsule, then the distortion will be recorded going into your 32-bit audio, thus leaving you with a distorted signal.
If you would like more information, please check out: https://www.sounddevices.com/32-bit-float-files-explained/
WHY WAIT WORKSHOPS
Kick Start Your Education with MediaTech Program Workshops. Every semester, we announce new workshops that highlight current and relevant topics in the media arts & entertainment industry. Check out MediaTech Events page regularly and follow our Facebook page for the upt-to-the-minute events details.